Performance regulation and biomedical application of near-infrared quantum dots
近紅外量子點的合成方法:近紅外量子點是一種具有在近紅外區域發射熒光的納米材料,其發射波長可以通過控制其大小、形狀、組成和殼層等因素來調節。常用的合成方法有熱解法、水熱法、微波法、溶劑熱法等。
近紅外量子點的表面修飾:近紅外量子點的表面修飾是為了提高其穩定性、分散性、生物相容性和靶向性,以及增加其功能性基團。常用的表面修飾劑有有機配體、無機殼層、聚合物、生物分子等。
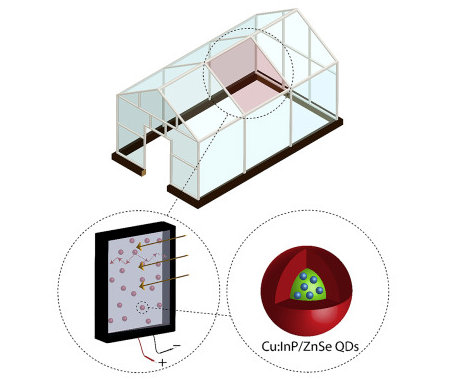
近紅外量子點的生物醫學應用:近紅外量子點由于其高熒光量子產率、窄發射峰寬、長熒光壽命和低自身熒光背景等優點,被廣泛應用于生物醫學領域,如生物傳感 、生物成像 、光動力治療 、光熱治療等。
Synthesis method of near infrared quantum dot: Near infrared quantum dot is a kind of nanomaterials with fluorescence emission in the near infrared region, whose emission wavelength can be adjusted by controlling its size, shape, composition and shell. The commonly used synthesis methods include pyrolysis method, hydrothermal method, microwave method, solvent thermal method and so on. Surface modification of near-infrared quantum dots: The surface modification of near-infrared quantum dots is designed to improve their stability, dispersion, biocompatibility and targeting, as well as to increase their functional groups. Commonly used surface modifiers include organic ligands, inorganic shell, polymers, biomolecules, etc. Biomedical applications of near-infrared quantum dots: Near-infrared quantum dots are widely used in biomedical fields, such as biological sensing, biological imaging, photodynamic therapy, and photothermal therapy, due to their advantages of high fluorescence quantum yield, narrow emission peak width, long fluorescence lifetime and low autofluorescence background.

Reference Documentation:
[1]Wang, X., Qu, L., Zhang, J., Peng, X., & Xiao, M. (2016). Near-infrared light controlled photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots for highly selective oxidation reaction. Nanoscale, 8(15), 8005-8014.
[2]Li, H., Kang, Z., Liu, Y., & Lee, S. T. (2012). Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(46), 24230-24253.
[3]Liang, W., Chen, M., Tu, D., Chen, X., & Yang, Z. (2020). NIR-II emitting CuInSe2/ZnS quantum dots for in vivo tumor targeting imaging and image-guided surgery. Nano Today, 35, 100941.
18915694570
Previous: Intracellular in situ
Next: BK Oncolytic virus pla