24.Design, synthesis and bioimaging applications of aromatic-ring AIE fluorescent nanoparticles based on β -cyclodextrin
AIE 型熒光納米粒子是一種利用聚集誘導發(fā)光(AIE)現(xiàn)象的納米材料,具有高熒光量子產(chǎn)率、高穩(wěn)定性、低背景信號等優(yōu)點,可以用于生物成像、傳感、顯示等領域。
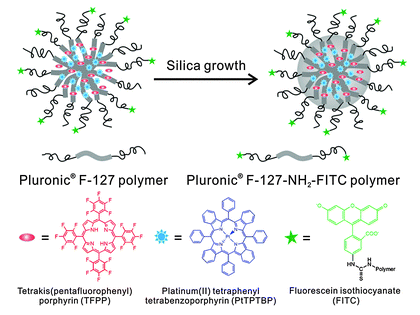
β-環(huán)糊精是一種具有內(nèi)腔疏水、外腔親水的大環(huán)超分子主體,可以通過包合作用與多種分子形成超分子復合物,改善其溶解性、穩(wěn)定性、選擇性等性質(zhì)。
通過在 β-環(huán)糊精上引入無芳香環(huán)的 AIE 分子,可以構建出具有高亮度、高選擇性、高生物相容性的 AIE 型熒光納米粒子,用于檢測和成像生物體內(nèi)的不同靶標。
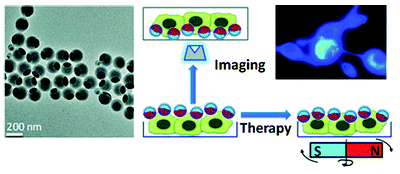
利用基于 β-環(huán)糊精的無芳香環(huán) AIE 型熒光納米粒子實現(xiàn)對動脈粥樣硬化(AS)的早期檢測和藥物篩選。利用一種含有羅丹明結構單元的無芳香環(huán) AIE 分子(Rho-AIE)與 β-環(huán)糊精通過包合作用形成超分子納米粒子(Rho-AIE@CD),并通過靜電吸附將其負載在陽離子型聚乙二醇(cPEG)上,制備出具有高亮度和高穩(wěn)定性的熒光探針(Rho-AIE@CD-cPEG)。該熒光探針可以特異性地識別和標記 AS 患者血清中的氧化低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL),并在近紅外區(qū)域發(fā)出強烈的熒光信號,實現(xiàn)對 AS 的早期診斷。同時,該熒光探針還可以與 AS 治療藥物西地那非(SDF)形成超分子復合物(Rho-AIE@CD-cPEG-SDF),并通過靶向輸送到 AS 斑塊處,釋放出 SDF 藥物,抑制 AS 的進展。該技術為 AS 的早期檢測和治療提供了一種新型的 AIE 型熒光納米平臺。
AIE type fluorescent nanoparticles are a kind of nanomaterials using aggregation-induced luminescence (AIE) phenomenon. With the advantages of high fluorescence quantum yield, high stability and low background signal, they can be used in biological imaging, sensing, display and other fields. β -Cyclodextrin is a large cyclic supramolecular body with hydrophobic and hydrophilic in the inner cavity. It can form supramolecular complexes with various molecules through package cooperation and improve its solubility, stability, selectivity and other properties. By introducing AIE molecules on β -cyclodextrins, AIE type fluorescent nanoparticles with high brightness, high selectivity and high biocompatibility can be constructed for the detection and imaging of different targets in the organism. Early detection and drug screening of atherosclerosis (AS) is achieved using aromatic-ring AIE fluorescent nanoparticles based on β -cyclodextrin. Using a non-aromatic ring AIE molecule (Rho-AIE) and β -cyodextrin formed ultra-molecular nanoparticles (Rho-AIE @ CD) and loaded on cationic polyethylene glycol (cPEG) by electrostatic adsorption to produce a fluorescent probe (Rho-AIE @ CD-cPEG). This fluorescent probe can specifically identify and label the oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) in the serum of AS patients, and emit a strong fluorescent signal in the near-infrared region, realizing the early diagnosis of AS. At the same time, the fluorescent probe can also form a supramolecular complex (Rho-AIE @ CD-cPEG-SDF) with the AS therapeutic sildenafil (SDF), which is targeted delivered to release SDF drugs to inhibit the progression of AS. This technique provides a novel AIE type fluorescent nanoplatform for the early detection and treatment of AS.
Reference Documentation:
[1]Mei J, Leung N L C, Kwok R T K, et al. Aggregation-induced emission: together we shine, united we soar![J]. Chemical reviews, 2015, 115(21): 11718-11940. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00263
[2]García R, Martín C, de la Fuente J M. Cyclodextrin-based nanomaterials for therapeutic and diagnostic applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(15): 5615-5635. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/cs/c8cs00176a
[3]Wang K, Ding D, Tang B Z. Highly Bright AIE Nanoparticles by Regulating the Substituent of Rhodanine for Precise Early Detection of Atherosclerosis and Drug Screening[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(4): 2005988. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005988
18915694570
Previous: Intracellular in situ
Next: BK Oncolytic virus pla